World Tuberculosis (TB) Day – 2025
Towards a TB-Free India
| “The decline in TB incidence is an outcome of India’s dedicated and innovative efforts. Through a collective spirit, we will keep working towards a TB-free India.”Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi |
Introduction
World Tuberculosis (TB) Day is observed every year on March 24th to raise awareness about the need to eliminate TB, the world’s deadliest infectious disease. The day marks the discovery of the TB-causing bacterium by Dr. Robert Koch in 1882. India has been observing this day since 1982, along with the global community. Despite progress, TB still impacts millions, posing serious health, social, and economic challenges.[3] This year’s theme, “Yes! We Can End TB: Commit, Invest, Deliver”, highlights the importance of stronger commitments and action, especially against rising drug-resistant TB.

India’s goal to eliminate TB by 2025 is one of the world’s most ambitious health missions. Under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), India has strengthened its TB response with advanced diagnostics, innovative policies, private sector partnerships, and a patient-first approach. Key drivers include record-high case reporting, better diagnostics, financial support for patients, and strong multi-sector collaboration. However, with global TB funding declining and shifting priorities, continued commitment is vital to meet India’s 2025 target and the UN’s goal of ending TB by 2030.
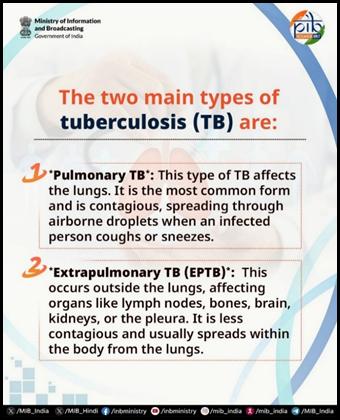
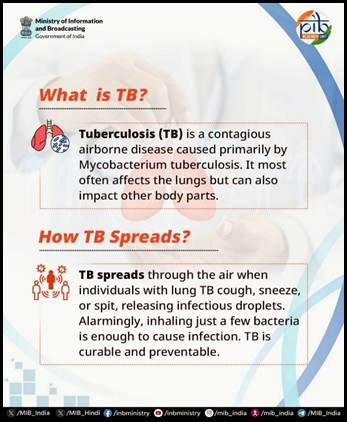
Despite global efforts, TB remains a major public health challenge worldwide, with India bearing the highest burden. Understanding both the global and national estimates is key to gauging the scale of the disease and the urgency of India’s elimination mission.


KEY INITIATIVES BY THE INDIAN GOVERNMENT TO ELIMINATE TB
To tackle this significant burden, the Government of India has implemented a range of focused strategies under its National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP). These key initiatives under NTEP aim to strengthen diagnosis, treatment, and prevention efforts, accelerating progress toward a TB-free India.
National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP)
In 2020, the Government of India renamed the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program (RNTCP) the National TB Elimination Program (NTEP). This reflects India’s goal to eliminate tuberculosis (TB) by 2025, five years before the global target of 2030. Here are the key targets for the Eradication of TB

The NTEP follows the National Strategic Plan (2017-2025), focusing on four key actions:
Detect – Treat – Prevent – Build (DTPB) to control and eliminate TB in India.
Objectives
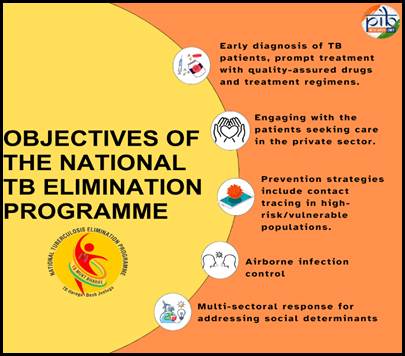
Achievements of the NTEP Programme
The NTEP is making strong strides toward eliminating TB by 2025. Here are its key achievements:
| The programme recorded its highest-ever case notifications, reporting 25.5 lakh TB cases in 2023 and 26.07 lakh cases in 2024. |
| First-Ever Indigenious TB Burden Model: India’s own mathematical model for state-wise TB estimates. |
| Incentives for ASHAs, TB Champions & Caregivers: Strengthening patient support systems. |
| 3 Lakh Additional Cases Found via House-to-House Screening: Focus on high-risk groups. |
| Medical College Task Force Active: 560 colleges supporting TB detection & research. |
| Sub-National Disease-Free Certification Implemented: Regular surveys, drug sales tracking, and under-reporting assessments. |
| Strong Multi-Sectoral Partnerships: Collaboration with ministries, industries, NGOs & technical bodies. |
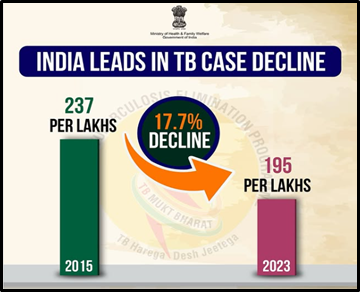
According to WHO’s Global TB Report, India has made significant progress in fighting tuberculosis. Under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), the incidence rate of TB cases have dropped by nearly 17.7%, from 237 cases per 1 lakh people in 2015 to 195 in 2023. TB-related deaths have also reduced, falling from 28 to 22 per 1 lakh people during the same period.
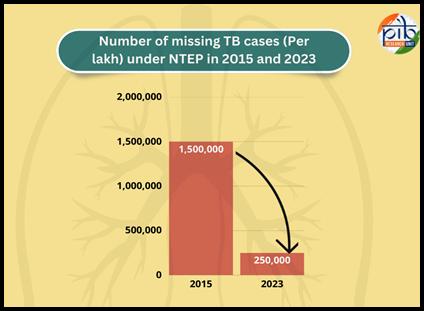
One of its key achievements has been reducing the number of missing TB cases from 15 lakh in 2015 to just 2.5 lakh in 2023 with a decrease of 83%.
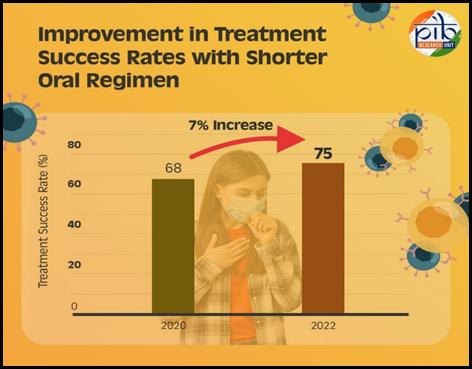
Under NTEP, India has rolled out improved drug-resistant TB treatments, including a safer, shorter all-oral Bedaquiline regimen, boosting success rates from 68% (2020) to 75% (2022). The mBPaL regimen (Bedaquiline, Pretomanid, Linezolid) offers 80% success for MDR-TB, cutting treatment to six months.
Components Of the NTEP Programme
Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (PMTBMBA)

The Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (PMTBMBA), one of the components of NTEP, aims to unite communities, businesses, and institutions to support TB patients and their families. It focuses on providing nutritional, diagnostic, and vocational support to improve treatment outcomes, reduce illness and deaths, and fast-track India’s goal of TB elimination. PMTBMBA is also recognized as the world’s largest crowd-sourcing initiative for nutritional support to TB patients.
Key goals include:
| Offering additional care and support to TB-affected individuals. |
| Promoting active community participation. |
| Mobilizing CSR contributions from businesses and institutions. |
Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana (NPY)
The NIKSHAY – TB Notification Incentive for the Private Sector, launched in 2018 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, incentivizes private healthcare providers to report TB cases, improving TB surveillance and treatment.
Under the Ni-Kshay Poshan Yojana (NPY), financial support for TB patients’ nutrition has been increased from ₹500 to ₹1,000 per month, providing ₹3,000 to ₹6,000 per patient throughout treatment. The patient must be registered and notified on the NIKSHAY portal.
The government has introduced Energy Dense Nutritional Supplementation (EDNS) for underweight TB patients (BMI < 18.5). Around 12 lakh patients will receive these supplements during the first two months of treatment to improve recovery rates and overall health outcomes.
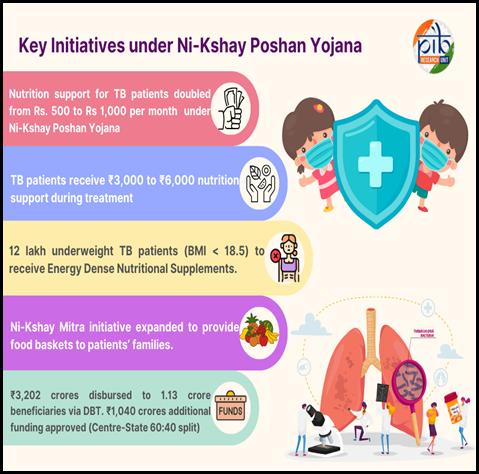
Ni-Kshay Mitra initiative – Under the Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (PMTBMBA), the Ni-Kshay Mitra initiative encourages individuals, NGOs, corporates, faith-based organizations, and others to adopt TB patients for at least six months, offering them nutritional, social, or economic support.
The scope of this initiative has now been expanded to include food baskets for household contacts of TB patients, aiming to boost immunity, lower infection risk, and reduce families’ financial burden. Additionally, over ₹3,202 crores have been disbursed to 1.13 crore beneficiaries through Direct Benefit Transfer under the Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NPY), supporting better nutrition and treatment outcomes. To further strengthen these efforts, the government has committed an additional ₹1,040 crores (shared 60:40 between Centre and States), ensuring enhanced support and reduced TB-related mortality.
Ni-kshay Portal
Ni-kshay Portal is a web-based patient management and surveillance system under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP). Developed by the Central TB Division, MoHFW, in collaboration with NIC and WHO India, it helps health workers in both public and private sectors to register TB cases, order tests, record treatment, monitor adherence, and transfer cases. It also serves as India’s National TB Surveillance System, ensuring real-time data reporting to the government.

Source – As of 23rd March, 2025 – https://dashboards.nikshay.in/community_support/overview
Over 1.51 crore TB patients are receiving treatment, with approximately 1.18 crore consenting to receive support. Around 1.18 crore commitments have been made by Ni-kshay Mitras, and over 2.59 lakh Mitras are registered. The initiative emphasizes public participation in TB elimination, resonating with the Prime Minister’s call for humanity. More details can be found on the Ni-kshay Dashboard.
Conclusion
India is making steady progress in its goal to eliminate TB by 2025 through focused interventions under the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP). Key initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (PMTBMBA) and Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana (NPY) are driving community participation and ensuring nutritional support, improving treatment adherence. The Ni-kshay Portal further strengthens surveillance and patient care. To sustain momentum, increased investments, innovation, and partnerships are crucial. With continued commitment, India is poised to become a global example in the fight against TB.
Andhra Pradesh Releases ₹1,200 Crore to Clear Scholarship and Fee Reimbursement Dues, Boosting Higher Education
In a major step to strengthen higher education and ease financial pressure on students, th…