First Operational Use of GBU-57 Bombs in Largest U.S. B-2 Bomber Strike Against Iran Nuclear Facilities.
The United States military executed Operation Midnight Hammer during the night of June 20 to 21, 2025, marking the largest operational strike ever conducted by U.S. Air Force B-2 Spirit bombers and the first combat deployment of the GBU-57 Massive Ordnance Penetrator bomb. Targeting Iran’s most fortified nuclear facilities at Fordow, Natanz, and Esfahan, this operation represents a milestone in strategic strike capability, involving a broad spectrum of integrated U.S. military platforms including stealth bombers, submarines, fifth-generation fighters, cruise missiles, and support from space, cyber, and transportation assets.
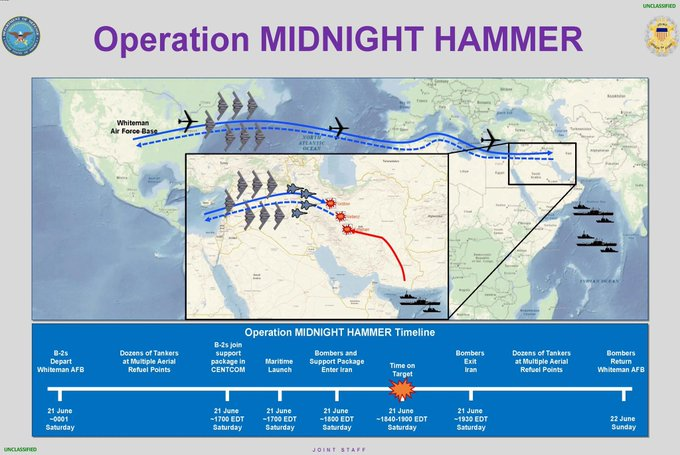
On June 22, 2025, six B-2s employed this 13,600-kilogram bunker-busting bomb in combat for the first time, striking Iran’s fortified nuclear enrichment sites at Fordow and Natanz in a coordinated U.S.-Israeli operation marking the official entry of the United States into the war against Iran. The operation was designed to degrade Iran’s nuclear infrastructure with precision, secrecy, and overwhelming force. It involved a strike package of seven U.S. Aitr Force B – 2 Spirit bombers, each crewed by two aviators and launched directly from the continental United States. This mission marked the longest B-2 sortie since the post-9/11 strikes and required multiple in-flight refuelling’s to complete its 18-hour round -trip.
The GBU-57A/B Massive Ordnance Penetrator is the most powerful conventional bunker-busting weapon in the U.S. arsenal. Weighing 30,000 pounds (13,600 kg), the bomb is over six meters in length and designed to penetrate up to 60 meters of earth or 18 meters of reinforced concrete before detonation. Developed by Boeing, the MOP is guided by a combination of GPS and inertial navigation systems, ensuring pinpoint accuracy. A total of 14 MOPs were dropped in this operation, all striking precise aim points at Fordow and Natanz to neutralise underground enrichment facilities that had been reinforced to withstand conventional attacks.
To maintain the element of surprise, the U.S. employed advanced deception tactics. A decoy formation of B-2s flew westward into the Pacific to mislead Iranian intelligence and early warning systems. Meanwhile, the actual strike package approached from the east, flying under strict emissions control to avoid detection. Just before the bombers entered Iranian airspace, a U.S. Navy submarine operating in the region launched over two dozen Tomahawk Land Attack Missiles (TLAMs) against Esfahan. These missiles targeted surface-level infrastructure and command-and-control centres, helping to blind Iranian radar systems and disrupt potential countermeasures.
The Tomahawk missile is a subsonic, long-range, all-weather cruise missile with a range exceeding 1,600 kilometres. It is capable of delivering a 450-kilogram high-explosive warhead with precision and is typically launched from surface ships or submarines. In this operation, the Tomahawks struck their targets just minutes before the B-2s released their payloads, ensuring complete tactical surprise and maximising impact on Iranian defence’s.
Air superiority and escort support were provided by U.S. fifth-generation fighters, including the F-22 Raptor and the F-35 Lightning II. These aircraft conducted suppression of enemy air defences (SEAD) by flying ahead of the strike formation and using electronic warfare systems and high-speed anti-radiation missiles (HARMs) to neutralise Iranian surface-to-air missile batteries and radar installations. The F-22, known for its unmatched agility and low observability, and the F-35, with its multi-role capabilities and network-centric warfare integration, ensured that Iranian defences could not engage the strike package as it entered and exited hostile airspace.
The entire operation required seamless coordination across multiple U.S. military commands. U.S. Strategic Command maintained oversight of global deterrence and nuclear posture. Transportation Command provided aerial refuelling through KC-135 and KC-46 tankers. U.S. Cyber Command likely disrupted Iranian communications and radar coordination electronically, while Space Command and the U.S. Space Force ensured real-time satellite intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance to track airspace conditions and enemy movements.
The B-2 bombers released their GBU-57s between 6:40 and 7:05 p.m. Eastern Time, which corresponds to approximately 2:10 a.m. local time in Iran. All munitions were confirmed to have struck their designated targets. Following weapons release, the aircraft exited Iranian airspace undetected and without encountering hostile fire. The operation demonstrated the ability of U.S. forces to conduct a high-risk, long-range strategic strike with absolute stealth, accuracy, and multi-domain support.
Operation Midnight Hammer represents a new benchmark in the application of precision strike power against nuclear proliferation threats. It demonstrated the operational maturity of the U.S. air Force B-2 Spirit bombers, the lethality of the GBU-57 bunker-buster bombs, and the strategic advantage of integrating stealth bombers, submarines, fifth-generation fighters, cruise missiles, space-based surveillance, and cyber capabilities into a single coordinated action. For the defence community worldwide, this operation has redefined the standards of modern strategic air warfare and showcased the United States’ ability to engage and neutralize hardened threats anywhere on the globe decisively.
Team Maverick.
Bangladesh Votes for Change as BNP Surges Ahead in Post-Hasina Election
Dhaka, Feb 2026 :Vote counting began in Bangladesh late Thursday after polling concluded f…




















